In this VHDL Example, I use ROL (Rotate Left) and ROR (Rotate Right) operators to chase the LEDs left or right. An input switch determines its chasing direction. A frequency divider is added to get a lower frequency driven from a NE555 square wave oscillator.
 |
| CPLD Hardware Test |
VHDL source is quite simple due to the rotate operators.
I assign all the I/O pin as follow.
#PACE: Start of PACE I/O Pin Assignments
NET "CLK" LOC = "P5" ;
NET "LED<0>" LOC = "P40" ;
NET "LED<1>" LOC = "P39" ;
NET "LED<2>" LOC = "P38" ;
NET "LED<3>" LOC = "P37" ;
NET "LED<4>" LOC = "P36" ;
NET "LED<5>" LOC = "P35" ;
NET "LED<6>" LOC = "P34" ;
NET "LED<7>" LOC = "P33" ;
NET "SEL" LOC = "P25" ;
#PACE: Start of PACE Area Constraints
#PACE: Start of PACE Prohibit Constraints
#PACE: End of Constraints generated by PACE
Each I/O device are already placed on the XC9536 CPLD Test Board.
Its RTL schematic is shown below.
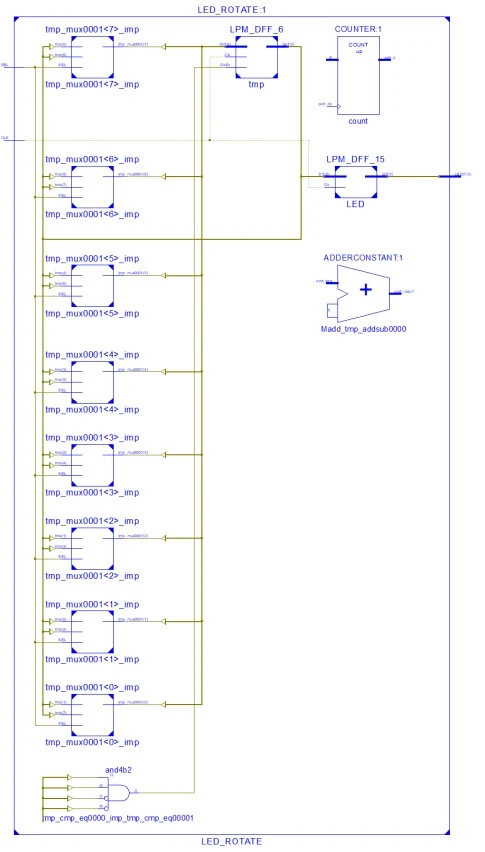 |
| RTL |
I use a Xilinx Parallel Cable III to program this CPLD.
 |
| iMPACT Device Programming Using Parallel Cable III |
It still work on a Desktop PC operated by Microsoft Windows 10.
Click here to download its source file.
No comments:
Post a Comment